NEUROSURGERY is a highly specialized surgical subspecialty that involves i) medical treatments ii) physical treatments iii) interventional or endovascular procedures and iv) minimally invasive microsurgeries for treating a very wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen at our BRAIN and SPINE. Among all, treating STROKE and PAIN are the basics of Neurosurgery daily practices.
In the other words, NEUROSURGEONs, with their knowledges and trainings, together with their sophisticated micro-instruments, utilize their operative skills under the microscope, they treat wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen along human nervous systems and its surrounding tissues; skull, spinal column, vessels and related tissues.
The followings are the summary of the common routines in Neurosurgical Practices:
with numbness, pain, weakness at arms or legs, sciatica pain at legs.
with spinal cord or cauda equina nerves compressions, causing pain, numbness, weakness at arms or legs, disturbed gait, disturbed urinary habit and bowel habits, disturbed sexual function.
with back pain, nerves compressions, spinal instability or scoliosis:
Minimally Invasive Spine Fusion Surgery under Microscope:Among all Neurosurgeries, minimally invasive spine surgery (MIS Spine Surgery) are the microsurgeries that Neurosurgeons most commonly perform among their routines.
For all spine surgeries, Neurosurgeons apply their knowledges of nervous system and spinal column, and also their microsurgical skills and techniques, together with their micro-instruments of brain surgeries. Sometimes, Neurosurgeons may also add the technique of Continuous Intra-Operative Neural Monitoring (IOM) to monitor the nerve signal transmission function along brain, spinal cord and nerves during surgery, so as to assure patients’ good neurological outcome in spine surgeries.
With the ever-advancing Medical Technology, seeking a second medical opinion is now the standard practice for all kinds of medical diagnoses. Getting a second medical opinion from another Medical Expert is a decision-support tool for ratification or modification of the medical suggestions from other doctors.
Second medical opinion may have critical impacts on the disease outcome by influencing the followings, namely 5Cs:
Brain tumors can be subdivided into non-cancerous benign tumor and malignant cancerous tumor. If a tumor is originated within brain compartment ......
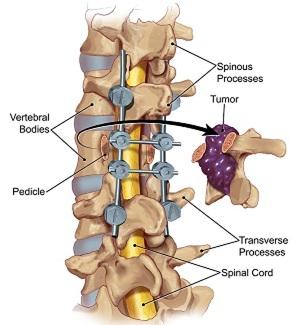
Tumors can develop in the vertebrae, nerves, and other tissue throughout your spine. Some spine tumors, such as astrocytomas, occur more commonly in children and adolescents......
Given the disease burden of strokes, prevention is an important public health concern. As stroke neurosurgeons, we do not want to treat stroke unless we are forced to do so for acute stroke ......
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness....
|
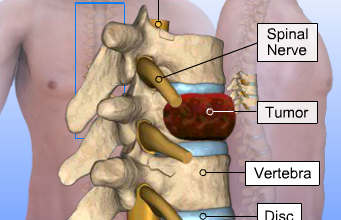
The spine, also called the backbone, is a flexible column of linked bones (vertebrae), muscles, tendons, and other tissues that extend from the base of the skull to the tailbone. It includes three protective membranes that encase the spinal cord and the fluid surrounding it. The spine provides structural support for the body and facilitates movements such as twisting and bending. The column of nerves in the spinal cord transmits signals to the brain to control movement, sensation, and bladder and bowel function. Tumors can develop in the vertebrae, nerves, and other tissue throughout your spine. Some spine tumors, such as astrocytomas, occur more commonly in children and adolescents Fewer than 10 percent of spine tumors begin in the spine. These tumors, called primary tumors, may be benign or low-grade, malignant growths that are slow growing, or high-grade tumors that grow very aggressively. The vast majority of spine tumors are metastatic. These tumors arise from cancer that begins in another part of the body, such as the lungs, breasts, colon, prostate, kidneys, or thyroid gland. Sarcomas – cancers of the bone, muscle, or connective tissue – can also spread to the spine. |
 |
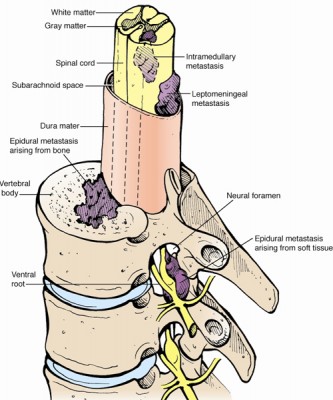 |
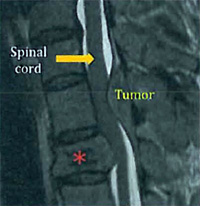
Spinal MetastasesMost primary and metastatic spine tumors are epidural tumors. These tumors grow in the bones of the spine. As they grow, they can compress the spinal dura – a thick sac that contains the spinal cord, nerve roots, and spinal fluid.
Nerve plexus tumors such as neurofibromas and ganglioneuromas occur next to the spine in the nerve plexus, a network of intersecting nerves that transmits signals from the brain to the arms or legs. |
As a spine tumor grows, it can replace bones or compress nerves, resulting in compression fractures or reduced blood supply to the spinal cord. Often, the first symptom of a spine tumor is the pain caused by these changes. The time of day at which the pain occurs can provide important information about the tumor.
Pain that occurs mainly when you are moving – mechanical pain – usually means that the tumor is causing weakness or instability in the bones of the spine.
Pain experienced primarily at night or in the early morning that lessens with movement is often an early sign that the tumor has spread. This is because your adrenal gland, which makes steroids during the day to help prevent inflammation, becomes less active when you are sleeping.
Spine tumors that are close to major nerves can disrupt the nerves’ ability to receive and send messages between the body and the brain. This can cause neurologic symptoms such as:
Tumors within the spinal cord generally cause detectable symptoms, while spinal tumors outside of the cord may develop for some time before symptoms emerge. Common symptoms include:
The first test to diagnose brain and spinal column tumors is a neurological examination. Special imaging techniques such as computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) are also performed.
Laboratory tests include the electroencephalogram (EEG) and the spinal tap. A biopsy, a surgical procedure in which a sample of tissue is taken from a suspected tumor, helps doctors diagnose the type of tumor.
Getting an accurate diagnosis for a spinal tumor is very important. It helps your doctor plan your care and may help increase the chance of successful treatment.
If you have symptoms that may signal a spinal tumor, your doctor (Neurosugeon) will examine you and ask you questions about your health, your lifestyle and your family medical history.