NEUROSURGERY is a highly specialized surgical subspecialty that involves i) medical treatments ii) physical treatments iii) interventional or endovascular procedures and iv) minimally invasive microsurgeries for treating a very wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen at our BRAIN and SPINE. Among all, treating STROKE and PAIN are the basics of Neurosurgery daily practices.
In the other words, NEUROSURGEONs, with their knowledges and trainings, together with their sophisticated micro-instruments, utilize their operative skills under the microscope, they treat wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen along human nervous systems and its surrounding tissues; skull, spinal column, vessels and related tissues.
The followings are the summary of the common routines in Neurosurgical Practices:
with numbness, pain, weakness at arms or legs, sciatica pain at legs.
with spinal cord or cauda equina nerves compressions, causing pain, numbness, weakness at arms or legs, disturbed gait, disturbed urinary habit and bowel habits, disturbed sexual function.
with back pain, nerves compressions, spinal instability or scoliosis:
Minimally Invasive Spine Fusion Surgery under Microscope:Among all Neurosurgeries, minimally invasive spine surgery (MIS Spine Surgery) are the microsurgeries that Neurosurgeons most commonly perform among their routines.
For all spine surgeries, Neurosurgeons apply their knowledges of nervous system and spinal column, and also their microsurgical skills and techniques, together with their micro-instruments of brain surgeries. Sometimes, Neurosurgeons may also add the technique of Continuous Intra-Operative Neural Monitoring (IOM) to monitor the nerve signal transmission function along brain, spinal cord and nerves during surgery, so as to assure patients’ good neurological outcome in spine surgeries.
With the ever-advancing Medical Technology, seeking a second medical opinion is now the standard practice for all kinds of medical diagnoses. Getting a second medical opinion from another Medical Expert is a decision-support tool for ratification or modification of the medical suggestions from other doctors.
Second medical opinion may have critical impacts on the disease outcome by influencing the followings, namely 5Cs:
Brain tumors can be subdivided into non-cancerous benign tumor and malignant cancerous tumor. If a tumor is originated within brain compartment ......
Tumors can develop in the vertebrae, nerves, and other tissue throughout your spine. Some spine tumors, such as astrocytomas, occur more commonly in children and adolescents......
Given the disease burden of strokes, prevention is an important public health concern. As stroke neurosurgeons, we do not want to treat stroke unless we are forced to do so for acute stroke ......
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness....
Cervical spine surgery may be indicated for:
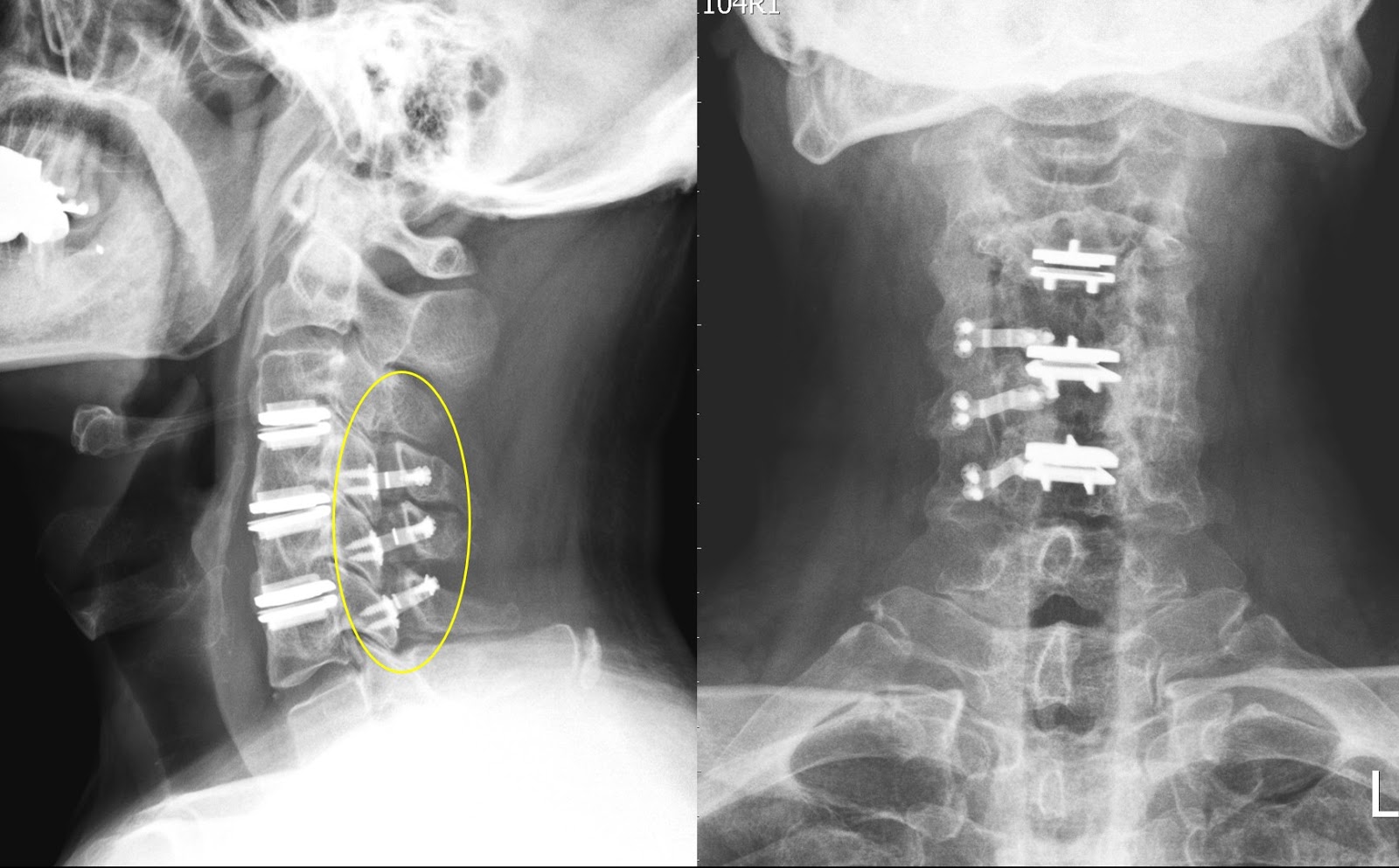
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion is a common surgical procedure used to treat neck problems such as bulging, herniated disc, degenerative disc disease and spinal instability etc. Discectomy is the removal of the disc and any fragments between the vertebrae. After the disc is removed, the space is filled with a bone graft, the goal is to help the bones to fuse together into one solid bone. This is known as fusion. In order to provide stability during fusion, the doctor may reinforce a metal plate screwed into the vertebrae (cage, screw and plate).The expected outcomes of this operation are to treat for symptoms due to cervical spondylosis aims to relieve pain and prevent further permanent damage to your nerves. Your mobility of neck will be reduced after fixing the disc.
The operation is performed under general anaesthesia. The approach to the cervical spine may vary with individual patient. It can be accessed from the front or from the back. X-ray may be used in the operation room to confirm the level of operation.
After the patient is awaken from the anesthesia, oral feeding may be started. A normal diet may be resumed as instructed after recovery from anaesthesia. Make sure there is no difficulty in swallowing when resuming normal diet. After general anaesthesia, you may experience discomfort in the throat after tracheal intubation. The side effects of anesthesia including feel tired, drowsy, nausea or vomiting. Inform the nurse if symptoms persist or worsen. You should inform the nurse of wound pain. Proper pain relief treatment by injection or oral medication may be prescribed by the doctor.
Patient would be discharge in 1-2 days when the patient can take oral food and pass urine by himself / herself with health condition.
In special patient groups, the actual risk may be different. Other complications may occasionally occur. For further information please contact our spine surgeon.

Lumbar spinal stenosis
Sacroiliac joint pain
Low back pain
Cervical Disc Hernia or Degeneration
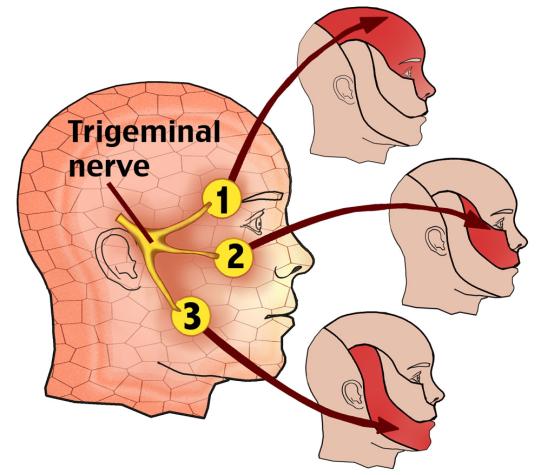
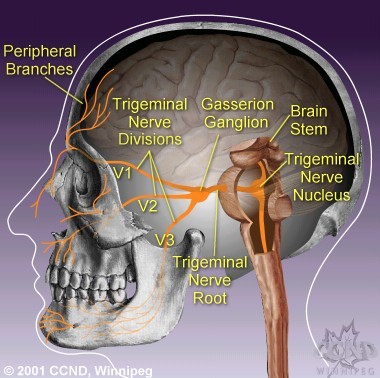
Trigeminal nerve is the 5th pair of cranial nerve at our brain. It contains mixed type of nerve fibers: general somatic sensory, visceral sensory fibers and motor fibers for muscle of mastication.
Trigeminal nerve thus controls the feeling of our face, mouth, nose and it also controls the movement of our masticatory muscle.
Trigeminal nerve sub-divides into the first Ophthalmic branch for the forehead region, the second maxillary branch for the cheek region and the third mandibular branch for the jaw region.
 |
 |
Primary:
Secondary:
Risk factors of developing primary trigeminal neuralgia
No indication or warning:
Sharp attack of pain, without any warning, usually at one side
Triggered by certain movements or the external factors: air flow, chewing, temperature changes, etc.
Short but intense:
Patients often describe the pain as burning, electric shock, needles, or stabbed by a knife, some cases may accompanied by other symptoms when pain appears:
e.g. facial muscle twitching, tearing, drooping of saliva, facial flushing, and conjunctival congestion, etc.
May be more serious:
As the disease progresses and worsens, disease-free intervals will be getting shorter and attacks become more frequent.
Characteristics of trigeminal neuralgia
Common trigger points:
Though diagnosis for neuropathic pain is not difficult, but there are often misdiagnoses.
We mainly rely on clinical judgment, but sometimes X ray, CT scan and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) do help in diagnosis.
In addition, doctors must exclude the possibility of tumors, such as Acoustic neuromas, Cholesteatoma, Hemangioma, Meningioma or Epidermoid cyst, etc.
The intervertebral disc serves to allow flexible movement of human spine and it also acts as a shock absorber or cushion.
It is composed of well-hydrated gel filled nucleus at its central and inner portion (like the same portion of a car’s tyre), and an outer annular fibrous layer (like the rubber outer layer of a tyre. 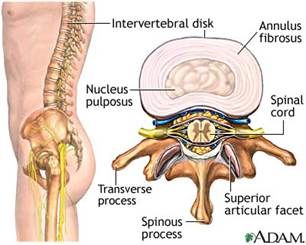
In many ways, the disc analogous to an automobile tyre. As long as the disc remains young, hydrated and being pressurized, it remains strong to support our body weight. A young and healthy disc will be revealed as a White Disc on MRI study of our spine in T2 image. 

However, due to the following reasons:
Our intervertebral disc may become dehydrated (water loss) or dry up at the central gel filled nucleus portion (become a black disc on MRI T2 images), it will depressurizes like to become an old flatten tyre. 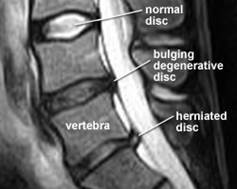
As soon as our disc depressurizes then problems may arise with the increased shear stresses developing on the outer side wall, just as one sees when a car tyre runs flat and fails. After then, depend on individual’s physical heath, various kinds of spine problem begin: 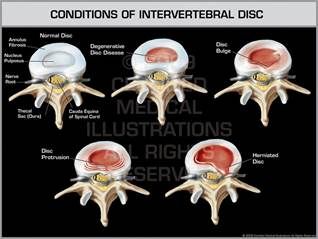

Various kinds of spine symptoms:
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness, visual blurring and epileptic seizure are the common presentating symptoms of brain tumour. Other symptoms vary and mainly depend on the location of tumor at different region of the brain to affect different brain functions.
Method of treating brain tumors include: steroids, anit-convulsants, surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Treatments can be single or combination of the above.
Prompt and early treatment
Prompt and early treatment of brain tumour can prevent or reduce neurological deficits. For example, steroid therapy to treat brain swelling and anti-convulsive medication to treat or prevent epileptic seizures.
Steroid therapy
Steroid can remove swelling or extra brain fluid of adjacent normal brain tissue around the tumour. It will make patients feel more comfortable and lead to dramatic symptomatic improvement. Steroid is usually used before, during and after surgery and radiotherapy.
Definite treatment
Choice of definite treatment for brain tumour depends on:
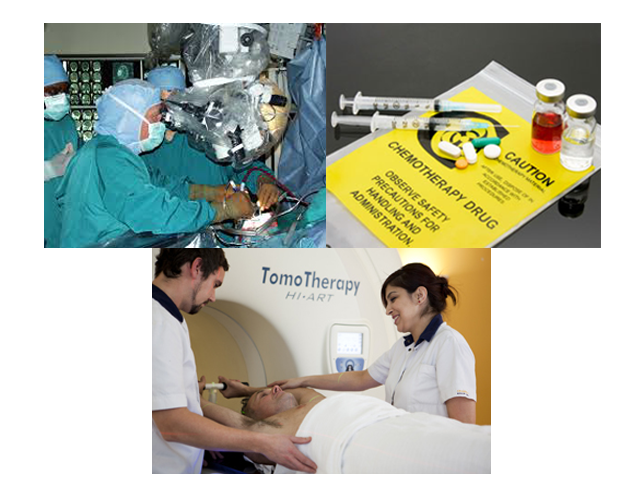
Surgery
Most benign brain tumor can be completely removed by surgery. For brain cancer, neurosurgeon may decide to remove part of the tumor in order to reduce the pressure on normal brain, so to improve patient's symptoms.
Brain tumor surgery, normal involve opening of skull bone, i.e. also known as craniotomy。 The surgery require general anesthesia, and usually require hair shaving. The aim of the surgery is to remove the tumor while preserving normal brain tissue and its vessels, so as to preserve normal brain function.
Highly malignant brain tumor - malignant glioma or Glial Blastoma Multiforme ( GBM) is well known brain cancer. Brain cancer, despite its invasive nature to surrounding brain, usually do no spread to other organs of the body i.e bone, lung or liver. However it will spread out finger-like extensions in all directions to invade surrounding important brain tissues such as motor area of the brain, brain stem, or even cross the midline to the opposite side of the brain. The invasion cause complete surgery tumor resection very difficult, and with considerable risks leading to serious neurological complications. In that instance, for patient safety and to preserve patient's intact neurological function, limited tumor resection to reduce intracranial pressure inside head, later supplemented by radiotherapy or chemotherapy is the best treatment option. Brain cancer cells may also spread to spine via cerebrospinal fluid.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is the use of high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells, making them unable to breed, while minimising the damages to surrounding healthy brain cells.
Brain cancer, after surgery, usually require whole brain radiation therapy. Radiotherapy is to be performed on daily basis over 4 weeks duration. Target chemotherapy may be given at the same time of radiation therapy to enhance treatment efficacy.
Radiosurgery ( i.e. Cyberknife, Gamma-knife, or X-knife ) is a kind of focal radiation treatment to small volume of tissue target i.e. tumour cells only. Its main application is for small benign tumour of less than 3 cm in size e.g. acoustic neuroma or inoperable deep seated benign tumor i.e. meningioma, etc.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells by disrupting the cycle of cancer cells growth and cell division. Sometimes it is used alone or combine with radiation therapy. Chemotherapy for brain tumors is usually given as outpatient basis.