NEUROSURGERY is a highly specialized surgical subspecialty that involves i) medical treatments ii) physical treatments iii) interventional or endovascular procedures and iv) minimally invasive microsurgeries for treating a very wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen at our BRAIN and SPINE. Among all, treating STROKE and PAIN are the basics of Neurosurgery daily practices.
In the other words, NEUROSURGEONs, with their knowledges and trainings, together with their sophisticated micro-instruments, utilize their operative skills under the microscope, they treat wide spectrum of clinical conditions and diseases that happen along human nervous systems and its surrounding tissues; skull, spinal column, vessels and related tissues.
The followings are the summary of the common routines in Neurosurgical Practices:
with numbness, pain, weakness at arms or legs, sciatica pain at legs.
with spinal cord or cauda equina nerves compressions, causing pain, numbness, weakness at arms or legs, disturbed gait, disturbed urinary habit and bowel habits, disturbed sexual function.
with back pain, nerves compressions, spinal instability or scoliosis:
Minimally Invasive Spine Fusion Surgery under Microscope:Among all Neurosurgeries, minimally invasive spine surgery (MIS Spine Surgery) are the microsurgeries that Neurosurgeons most commonly perform among their routines.
For all spine surgeries, Neurosurgeons apply their knowledges of nervous system and spinal column, and also their microsurgical skills and techniques, together with their micro-instruments of brain surgeries. Sometimes, Neurosurgeons may also add the technique of Continuous Intra-Operative Neural Monitoring (IOM) to monitor the nerve signal transmission function along brain, spinal cord and nerves during surgery, so as to assure patients’ good neurological outcome in spine surgeries.
With the ever-advancing Medical Technology, seeking a second medical opinion is now the standard practice for all kinds of medical diagnoses. Getting a second medical opinion from another Medical Expert is a decision-support tool for ratification or modification of the medical suggestions from other doctors.
Second medical opinion may have critical impacts on the disease outcome by influencing the followings, namely 5Cs:
Brain tumors can be subdivided into non-cancerous benign tumor and malignant cancerous tumor. If a tumor is originated within brain compartment ......
Tumors can develop in the vertebrae, nerves, and other tissue throughout your spine. Some spine tumors, such as astrocytomas, occur more commonly in children and adolescents......
Given the disease burden of strokes, prevention is an important public health concern. As stroke neurosurgeons, we do not want to treat stroke unless we are forced to do so for acute stroke ......
Brain tumors grow and compress normal brain tissue. Both benign and malignant tumors can cause swelling of the brain and raised intracranial pressure. Headache, dizziness....
|
Interventional Pain Management
Pain is a multidimensional experience. Chronic pain differs from acute pain in that it lasts for more than 3-6 months, and there may not be obvious tissue injury leading to the pain. The pathway leading from stimulus to perception may be sensitised [1]. There is often associated depression. Management of chronic pain therefore requires a holistic multi-disciplinary approach [2]. In addition to pharmacological treatment, psychosocial support, physiotherapy and operative treatment, interventional techniques may benefit some patients by defining the pain generator and offers prolonged relief.
Interventional Pain Procedures Commonly performed interventional procedures for pain of spinal origin include trigger point injections, facet blocks, sacroiliac joint blocks, epidural steroids and epidural lysis. Blocks with local anaesthetics identify the source of pain when pain level is reduced significantly after the block. Local administration of steroids decreases inflammation. Denervation by a radiofrequency current can bring prolonged relief by interrupting the sensory pathway. A very small group of selected patients benefits from spinal cord stimulation or insertion of an intra-thecal drug delivery system. Diagnostic blocks with a local anaesthetic help to ascertain the source of pain. Back & Neck Pain Facet joints are small synovial joint connecting the posterior aspects of the vertebrae. Inflammation of these joints or abnormal stress on them can lead to facet joint pain. There are back or neck pain with radiation, but no radicular symptoms. Pain typically worsens on extension. Facet pain syndrome often co-exists with disc pathologies [3]. These joints are supplied by medial branches of adjacent spinal segments. Diagnostic blocks are performed by injection of the joints or the medial branches under fluoroscopy. Joint injections can be supplemented by local steroids. Longer term effect is achieved by radiofrequency lesioning of the medial branches [4,5] (Fig.1).
Sacro-Iliac Joint Pain
Sacroiliac joint pain presents with back pain, usually to the side of lesion, with radiation to the groin or the knee. Bilateral joint involvement may present as central back pain. Interventional treatment approach is similar to facet joint pain [6,7]. More recently developed Cooled Radiofrequency technique produces more consistent lesions for the multiple sacral nerves [8]. Sciatica Radiculopathy presents with back or neck pain with radiation. Lesions in the lumbar levels produce the familiar ‘sciatica’ symptoms, whereas cervical lesions cause pain radiating to the shoulder or upper limb. Radicular pain may be caused by pressure or irritation of the nerve roots by degenerated intervertebral discs. Nerve impingement may also be caused by spinal stenosis, spondylolisthesis or failed back surgery syndrome. Injection of steroids into the epidural space may help these patients. The approaches may be translaminar, transforaminal or caudal [9,10] (Fig. 3). If multiple levels involvement is suspected or for resistant cases, a specially designed Racz catheter can be introduced from the sacral hiatus to define the levels of nerve impingement on epidurogram [11]. Hydrodissection is performed and steroid is deposited [12] (Fig. 4).
Spinal Cord Stimulation
Melzack and Wall proposed the gate-control theory in 1965 [13]. The concept of stimulation of large afferent fibres to close the ‘gate’ for pain perception lead to the development of spinal cord stimulation. Shealy published the application of ‘dorsal column stimulation’ in 1967 [14]. Over the years spinal cord stimulation has developed into a percutaneous technique where a lead with multiple contact points is inserted into the epidural space and is connected to an implanted pulse generator. Programmable electric current stimulates the spinal cord, leading to pain relief. This is particularly useful for very carefully selected patients who suffer from failed back surgery syndrome [15] or arachnoiditi. (Fig.4) Intrathecal Drug Delivery Systems
Implantable intrathecal drug delivery systems are available for delivery of medications such as opioids or baclofen into the subarachnoid space directly. This may be of use for some very selected patients [16]. References
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fig 1 a - g. The procedures of mechanical thrombectomy |
||
| a. Pretreatment angiography shows total occlusion of the M1 segment of the left middle cerebral artery (MCA) (arrow). b and c. Angiogram and illustration of the procedure show the occlusion site and surrounding angioarchitecture. d. Immediate post-procedural angiography shows complete revascularisation (arrow). e. Large syringe is connected to the reperfusion catheter with forceful suction. f. Disrupted clot removed out from body. g. Retrieved whole clot |
 |
||
| Fig 2. Total stroke cost in US |
|
|
 |
|
| Fig 3. The Wingspan system of intracranial vascular stent | ||
|
|
||
|
Fig 4a. The Pre-stenting angiogram (DSA) showing right MCA stenosis.
b. stent-in-situ with stent marker (white arrow) c. the post-stenting DSA
|
||
Management of Acute Stroke (TPP-3D8P):
Time--Place--Person--3 Golden hours Drug or PCI—8 Golden Hours only PCI (TPP-3D8P)
1. Time:
b. Promptly seek for emergency help during the Golden-3-Hours therapeutic window.
2. Place: Seek immediate medical assessment and treatment in Hospital equipped with CT scanner, MRI scanner and Angiogram machine.[16]
3. Person: Seek help from vascular neurosurgeon who can provide comprehensive treatment and who can manage the complications associated with ischaemic stroke and its treatment.
4. 3-Golden-hours Drug or PCI:
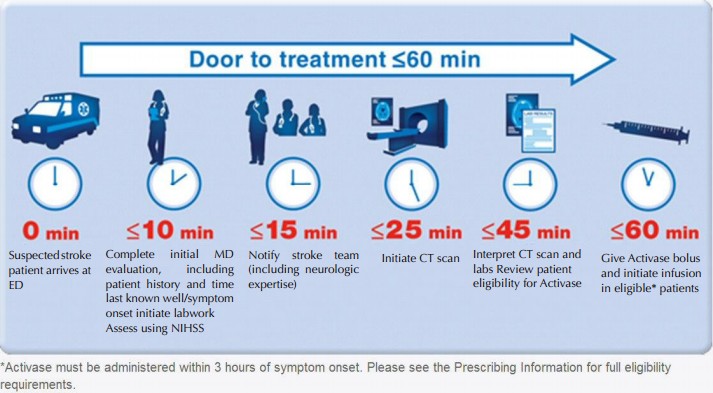 |
|||
| Fig 5. The Narrow time frame of the iv rtPA Therapy | |||
|
|
|||
 |
 |
 |
|
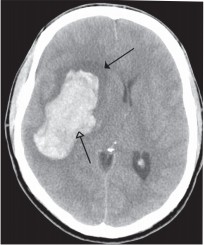
| Fig 6a. Typical dense string sign over Middle Cerebral Artery occlusion (arrow) | Fig 6b. CT angiogram confirm Middle Cerebral Artery occlusion over left side, while right side revealed normal Middle Cerebral Artery | Fig 7. Right capsular intracerebral haemorrhage (arrows) | |
 |
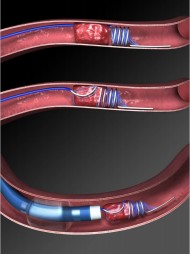 |
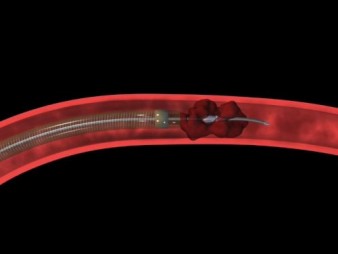
| Fig 8a. The Penumbra System for mechanical thrombectomy | Fig 8b. The Merci Clot retriever for mechanical thrombectomy |
 |
||
|
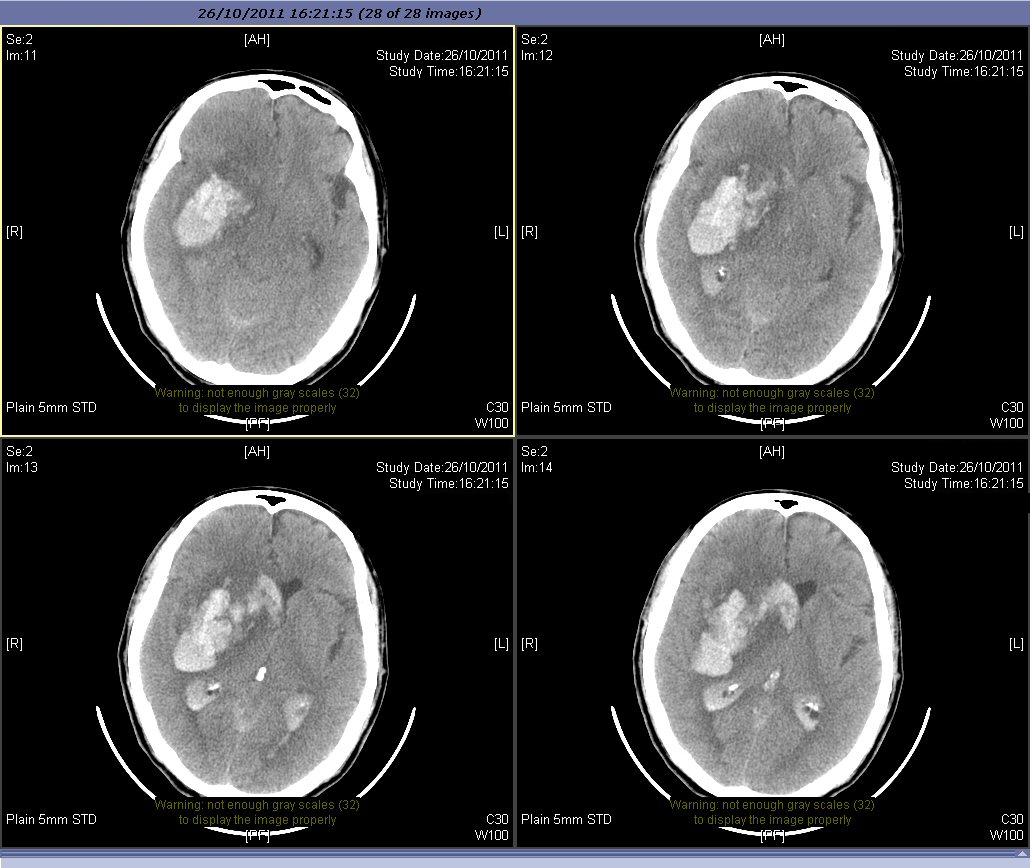
Fig 9a. Severe intracranial bleeding after iv rtPA
|
||
 |
 |
|
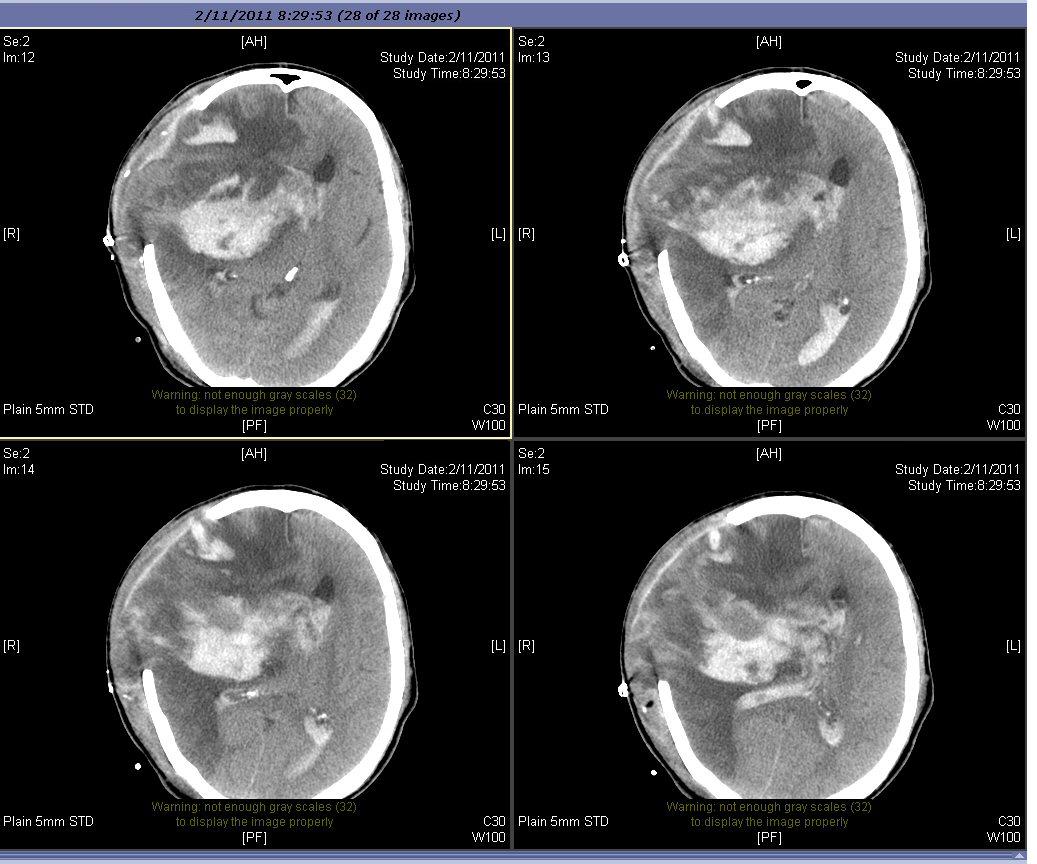
| Fig 9b. After surgery for blood clot removal and craniectomy | Fig 9c. The brain with gross shrinkage | |
|
|
|
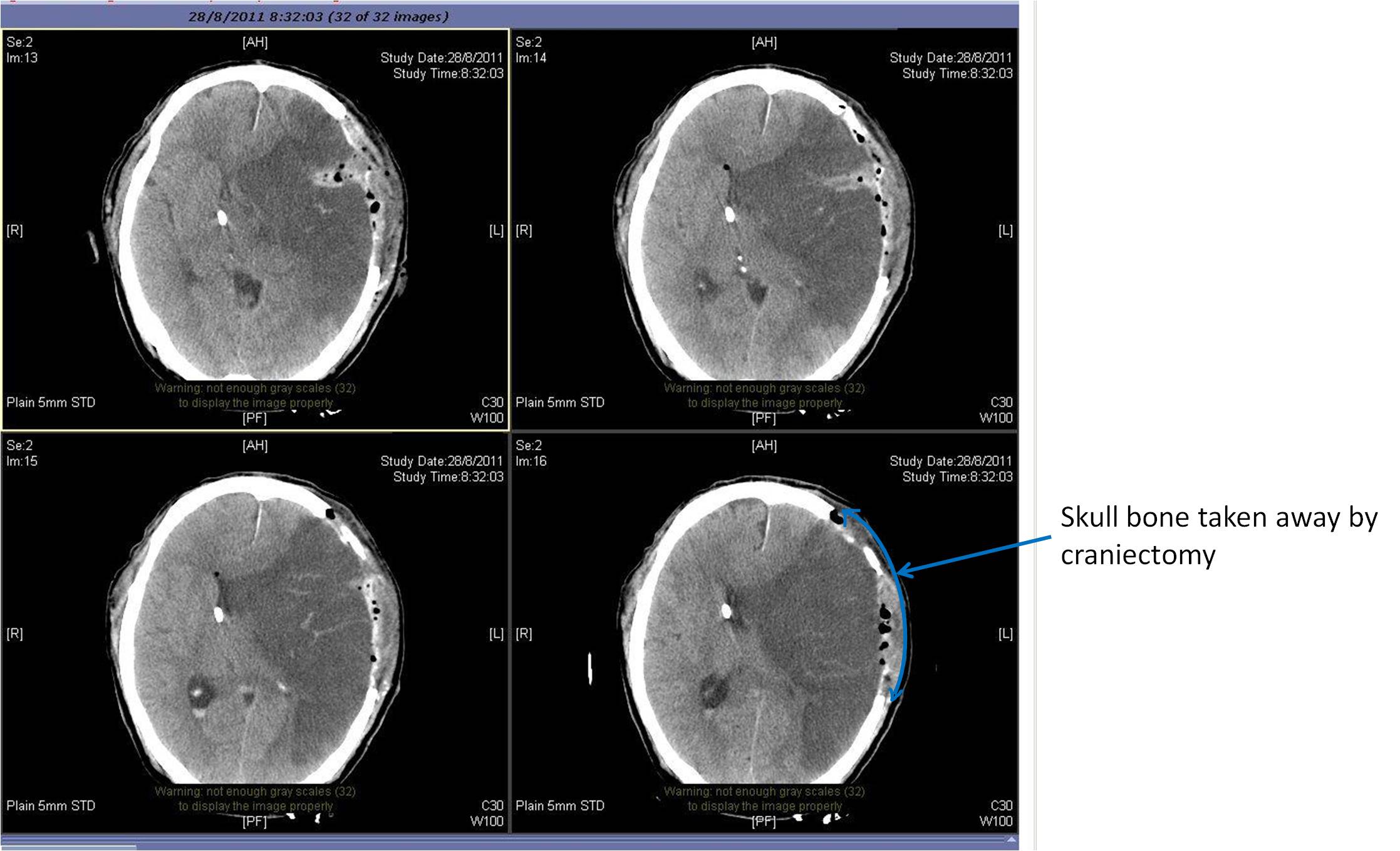
Fig 10a. Left MCA infarction with mass effect
|
 |
|
Fig 10b. Left sided decompressive craniectomy
|
 |
|
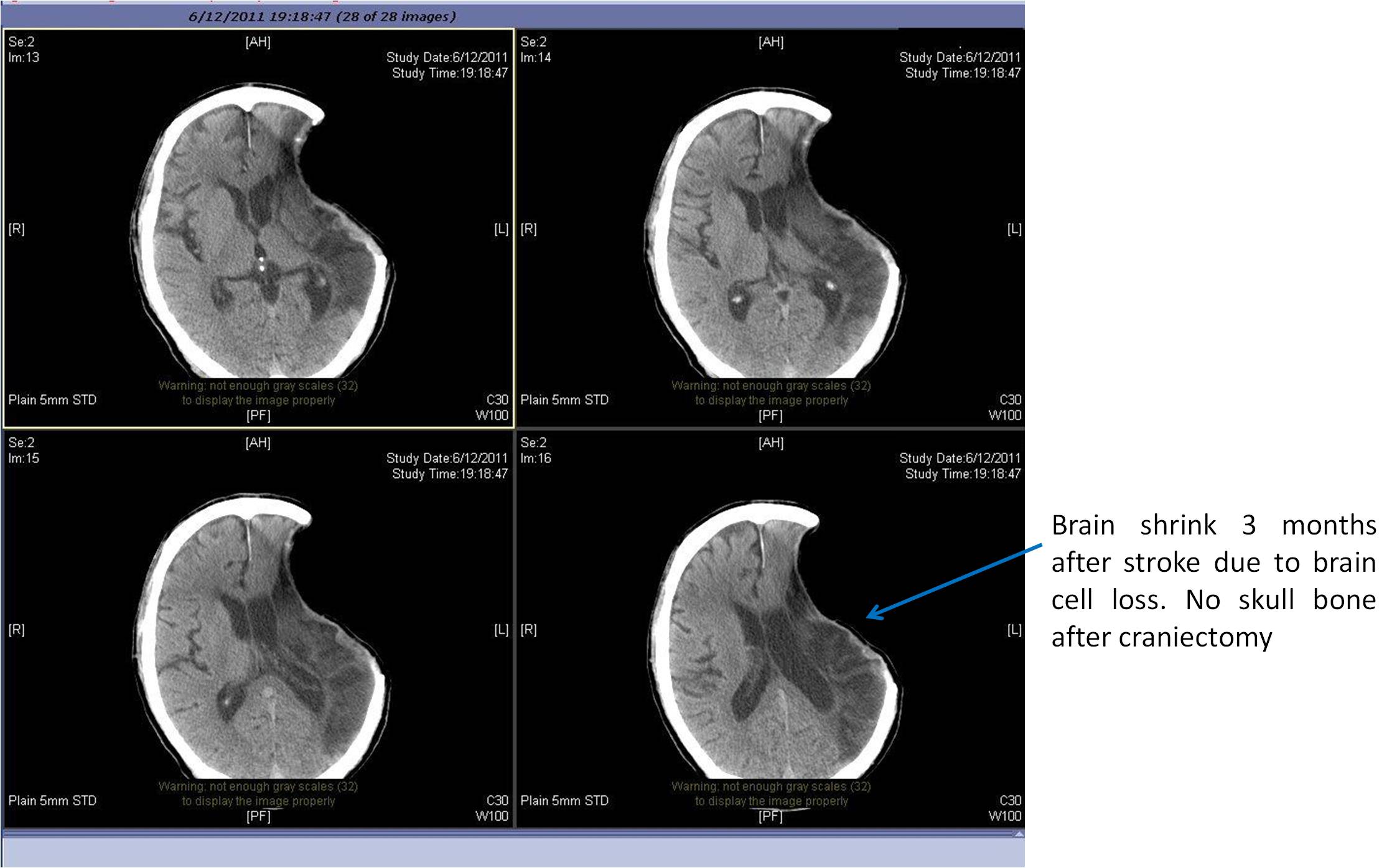
Fig 10c. Finally there is brain shrinkage
|
References